
We make "YOUR FUTURE"
folding
(Peptidyl prolyl isomerase)
(FK506 binding proteins)
Purvulin : Prokaryotes
Cyclophilin is one of the research themes of Caretis in the field of biomedical science.
Based on the above "Cyclophilin schematic daiagrm", we plan to serialize irregulary the prospects for implementatian that Caretis is interessted.
1st Schedule:What are peptidyl prolyl isomerase( PPlase )and chaperones?
2nd Schedule:Cyclophilin A
3rd Schedule:Cyclophilin D
What is cyclophilin?
Cyclophilin is a protein named after the protein to which the immunosuppressant cyclosporine used in organ transplantation binds,
and has peptidyl prolyl isomerase(PPlase)activity.
This PPlase is a type of isomerase that is present in all organisms and catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline residues in protein molecules.
What is peptidyl prolyl isomerase(PPlase)?
Peptide bonds between amino acides are generally much more stable in the trans form than in the cis form,
and this state is achieved naturally.
However, due to its unique structure, the N-side peptide bone exists relatively stably as a cis form in the proline residue.
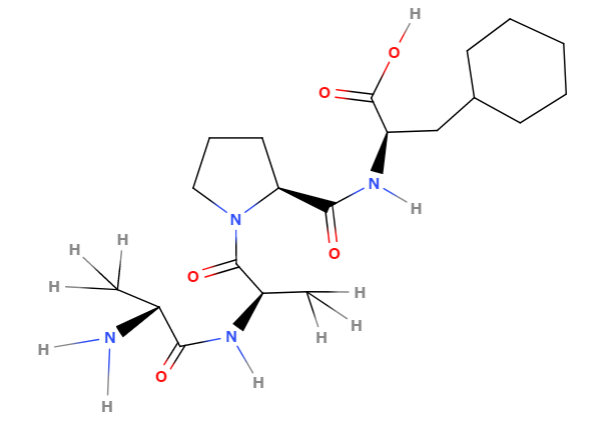
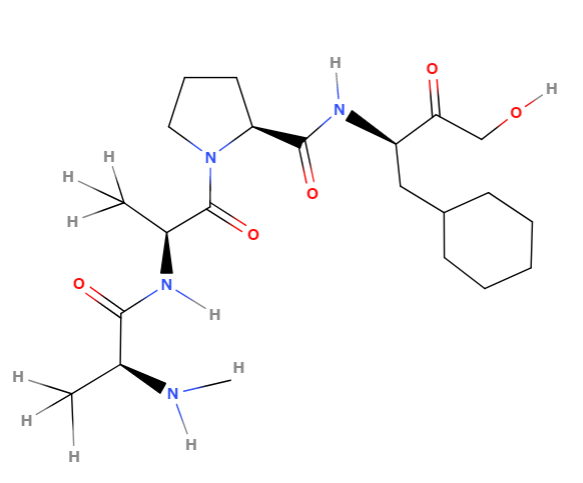
This is a structure formula creater by Molview of the substrate Ala-Ala-Pro-Phe when measuring the PPlase activity of cyclophilin.
Macromolecules such as proteins make larger structural differences in the cis-trans form.
cis
trans
This is a video showing the electron density
of ALa-Ala-Pro-Phe on an electrostatic potential map. Let's watch.
Protein, which are the main constituent molecules of living organisms and cells, are made up of amino acids,
but accurate folding of proteins is necessary for the proper functioning of proteins.
Since the activation energy required for cis-trans isomerization of this bond is relatively high at about 20 kcal/mol,
this bond is natturally difficult to isomerize, and folding requires that the isomerization of proline residues be catalyzed. There is.
Prolyl isomerase works here, so it can be said to be one of the chaperones.
Examples of prolyl isomerases includ eukaryotic cyclophilin, FKBP, Pin1, and prokaryotic parbrin.
Prolyl isomerases are also active against the same type of protein and promote self-folding.
Cyclophilin and FKBP are target proteins of certain immunosuppressive drugs and are collectively called immunophilin.
These are required for the expression of activity of several protein complexes involved in signal transduction, such as calcineurin,
which plays a central role in the regulation of the immune system. It can also interfere. However, this property may nat be directly related to prolyl isomerase activity.
Next, I will explain about chaperone.
What is a chaperone?
A general term for proteins that help other protein molecules to fold correctly and acquire function.
Also called molecular chaperone or protein chaperone.
Chaperones only provide an environment or opportunity for the formation of native structures, however the function of chaperones is not only to
assist folding, but also to control protein quality (complex formation, transport, refolding, deagglomeration).
Chaperones are indispensable because these functions are essential in life activities.
Abnormalities in molecular chaperones cause protein dysfunction involved in maintaining cell homeostasis.
Specifically, it is thought to be a factor in the progression of diseases such as metabolic system abnormalities, tumor progression,
neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular disorders.
Another way to look at it is that chaperones are essential for the proper and maintenance of conformation, binding interactions, localization
and concentration control (proteostasis) of individual proteins present in cells. It can be said that it is an element of.
Chaperones are classified as follows.
Heat shock response
Many chaperones are heat shock proteins (HSPs) that provide a heat shock response to prevent damage
from elevated temperatures. In other words, it controls the proper folding of a protein when it is denatured by heat.
Cold shock response
A grup of RNA-binding chaperones responsible for the cold shock response are called cold shock proteins(Csp)
(RNA chaperones). Csp unravels the extra secondary structure generated on RNA into a signal strand, enabling gene expression and protein synthesis.
Folding new Proeteins.
Most proteins fold without chaperones, but some require chaperones. If we limit the folding of newly synthesized polypeptide chains throug translation,
it is said that 30% of intracellulr proteins require chaperones.
The reson why many nascent polypeptide chains require chaperon is that freshly made hydrophobic amino residues are exposed to the surrounding water molcules (in nature, the hydrophocic residues are internal and surrounding.
It is said to be because it tries to bind to orther hydrophobic residues that it first encountered in order to escape from the water molecule (isolated from the water mollecule).
The neatest hydrophobic region is ofter not the original binding partner, and the randam interactions are likely to lead to incorrect folding.
Proteins that fail to fold in this way tend to aggregate, and the aggregated proteins are very harmful to cells (eg prion proteins that cause bovine spongiform encephalopathy and β-amyloid protein that causes Alzeimer's disease.)
It seems that there are many cases.
Chaperones serve to hide the hydrophobic protein of the nascent polypeptide from water molecules until the correct binding partner appears.
A normal chaperone has a pocket with a hydrophobic area inside, where the substrate is stored. The hydrophobic region of the substrate interacts with the hydrophobic region in the pocket and improper binding is suppressed.
Histon chaperone
Histone chaperone is a protein that binds histones to naked DNA to form nuceleosomes. The role of this protein is to restore the destabilized nucleosomes,
which are primarily histones removed from the chromatin duiring transcription. This destabilization is thought to be carried out by RNA polymerase in contact with the transcription
region inside the nucleosome to perform transcription, and the chromatin transcription promoter (FACT) is known as histone chaperone.
("About the chaperone" is quoted from the chaperone on Wikipedia.)
Cyclophilin A
Cyclophilin(CyP) is a family of immunophilins named for their ability to bind to cyclosporins.
CyP is a protein that is ubiwuitously distributed in the cytoplasm. The CyP-Cyclosporin complex inhibits the activity of calcium / calmodulin-depemdent phosphatase (calcineurin).
CyP has peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase (PPIase) activity and regulates protein folding and transportation.
In addition, it is considered that the main function of the cyclophilin A-cyclosprin complex is to suppress the production of the pre-inflammatory substances TNF-α and interleukin 2 by inhibiting calcineurin activity, and to suppress the rejection of transplanted organs.
CyPA was initially thought to function primarily as an intracellualar protein, but recent studies have also shown that CyPA is secreted by cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. Studise in animal models and humans to date have provided evidence eo support the important function of CyPA in some human diseases.
It is summarized in the table below.
| disease | basis |
 Heart disease Heart disease |
CyPA is an important determinant of cardiac hypertrophy, cardiac ischemia, and reperfusion injury and may be a useful biomaker of coronary artery disease. |
 Viral infection Viral infection |
CyPA has been shown to interact with HIV capsid proteins. CyPA inhibits influenza virus replication by promoting the degradation of M1 protein. CyPA regulates the replication of severe acute respiratory syndorome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) through binding to nucleocapsid proteins and uptake into particles. |
 Cancer Cancer |
CyPA ①helps cancer growth(p53 and HIFα) ②regulates cell cycle progression ③blocks apotosis ④promotes movement / infiltration of details and thus promotes cancer cell growth, metastasis, and drug resistance. It has been suggested to be involved in. |
| It is known that the disruption of blood-brain barrier (BBB) by CyPA induces inflammation which activated by nuclear factors kappa B (NF-κB) and MMP-9. | |
 Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) |
Secretory CyPA has been identified in extracellular fluid in RA patients. CyPA is known to be increased in synovial fluid in RA patients compared to knee osteoarthritis patients. |
| CyPA expression is dramatically increased in inflamed gingival tissue compared to healthy gingival tissue and is known to be localized to infiltrating macrophages and lymphocytes, osteoclasts and osteoblasts. CyPA is known to be localized in the cellular matrix of infiltrating cells and / or inflamed gingival junction cells. CyPA has been suggested to be involved in gingival tissue inflammation by inducing PBMC / neutrophili chemotaxis and TNF-α / IL-8 secretion. |
Cyclophilin D is present in the mitochondrial matrix and is thought to be a component of mitochondrial permeable transition pores (MPTP).
For example, in ischemic encephalopathy, the stimulus of ischemia causes a transient increase in intracelluar calcium conceneration,
which triggers the opening of MPTP and the release of cytochrome C, which permeates apoptosis, from the cristate into the cytoplasm.
Cyclosporine binds to cyclophilin D and suppresses the release of MPTPs.